Project information
- Category: Neural Network, Classification
- Source Data: Download
Project Details
Data Description
In this project, I used use CIFAR-10 dataset which consists of 50000 32*32 color images in 10 classes with 5000 images per class.
Here are 10 classes:

As the dataset has labeled the variable, it is supervised machine learning. Supervised machine learning a is type of machine learning that is trained on well-labeled training data. Labeled data means that training data is already tagged with correct output.
In this project, I will solve the problem using neural networks: convolutional neural networks (CNN) as it is a supervised algorithm which rely on training data to learn and improve their accuracy over time.
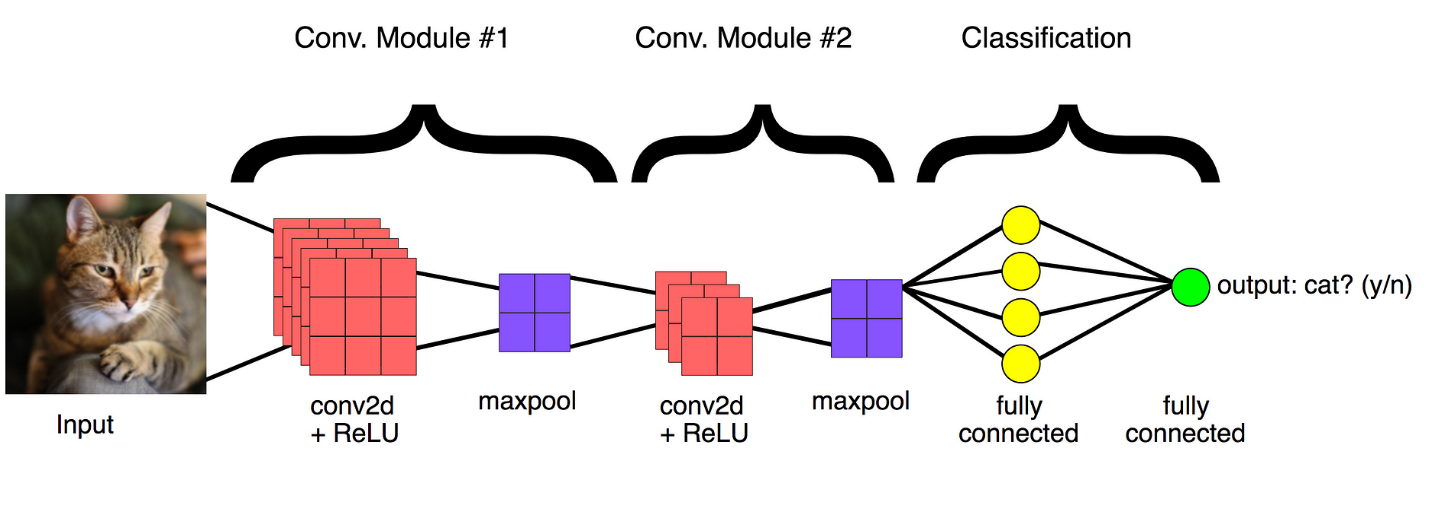
What is CNN?
CNN is a combination of Convolutional Layers and Neural Network. Convolution is nothing but a filter which is applied on an image to extract features from it. We will use such different convolutions to extract different features like edges highlighted patterns from the image.
Python Packages:
- Pandas
- Keras
- Numpy
- matplotlib
Roadmap:
Step 1:
Import packages:
from keras.models import Sequential from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator from keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Flatten, Dropout, BatchNormalization from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D import pandas as pd import numpy as np from keras.models import load_model import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ReduceLROnPlateau
def append_ext(fn):
return fn + ".png"
train_label_path = r'C:\Users\shang\Desktop\ML\data\image classification\trainLabels.csv' sub_file_path = r'C:\Users\shang\Desktop\ML\data\image classification\sampleSubmission.csv' train_folder_path=r'C:\Users\shang\Desktop\ML\data\image classification\train' test_folder_path=r'C:\Users\shang\Desktop\ML\data\image classification\test' traindf = pd.read_csv(train_label_path, dtype=str) testdf = pd.read_csv(sub_file_path, dtype=str) traindf["id"] = traindf["id"].apply(append_ext) testdf["id"] = testdf["id"].apply(append_ext)
Defined the path variable and then use read_csv to read data and automatically add file extension name.
Step2: Split a dataset into training and testing datasets
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1. / 255., validation_split=0.25)
Step3: Train the model
train_generator=datagen.flow_from_dataframe(
dataframe=traindf,
directory=train_folder_path,
x_col="id",
y_col="label",
subset="training",
batch_size=32,
seed=42,
shuffle=True,
class_mode="categorical",
target_size=(32,32))
valid_generator=datagen.flow_from_dataframe(
dataframe=traindf,
directory=train_folder_path,
x_col="id",
y_col="label",
subset="validation",
batch_size=32,
seed=42,
shuffle=True,
class_mode="categorical",
target_size=(32,32))
test_datagen=ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255.)
test_generator=test_datagen.flow_from_dataframe(
dataframe=testdf,
directory=test_folder_path,
x_col="id",
y_col=None,
batch_size=32,
seed=42,
shuffle=False,
class_mode=None,
target_size=(32,32))
earlystop = EarlyStopping(patience=10) learning_rate_reduction = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_accuracy', patience=2, verbose=1, factor=0.5, min_lr=0.00001) callbacks = [earlystop, learning_rate_reduction]
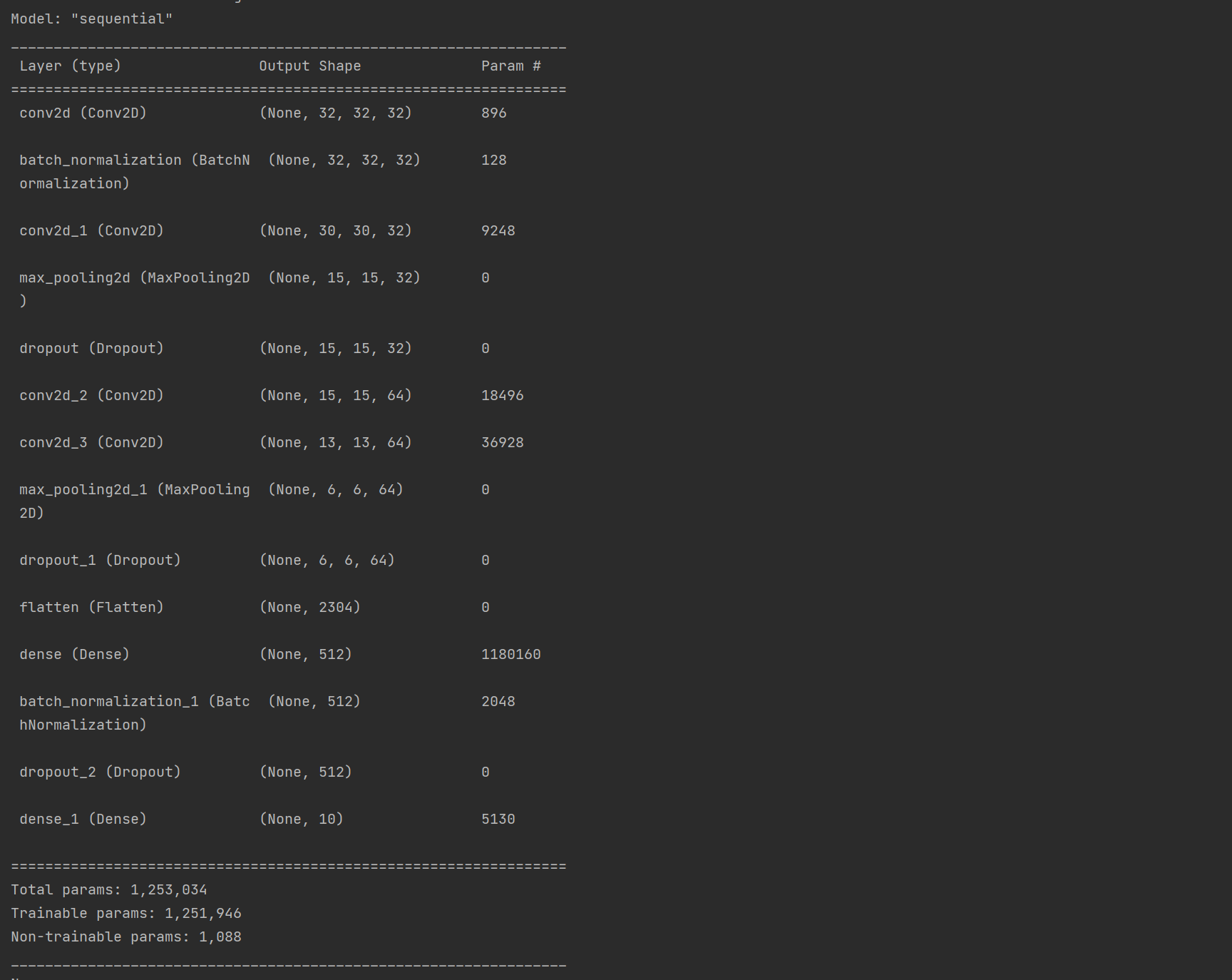
model = Sequential() model.add(Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same',input_shape=(32,32,3))) model.add(BatchNormalization()) model.add(Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu')) model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))) model.add(Dropout(0.25)) model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu',padding='same')) model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu')) model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))) model.add(Dropout(0.25)) model.add(Flatten()) model.add(Dense(512, activation='relu')) model.add(BatchNormalization()) model.add(Dropout(0.5)) model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax')) model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy']) print(model.summary())
STEP_SIZE_TRAIN=train_generator.n//train_generator.batch_size
STEP_SIZE_VALID=valid_generator.n//valid_generator.batch_size
STEP_SIZE_TEST=test_generator.n//test_generator.batch_size
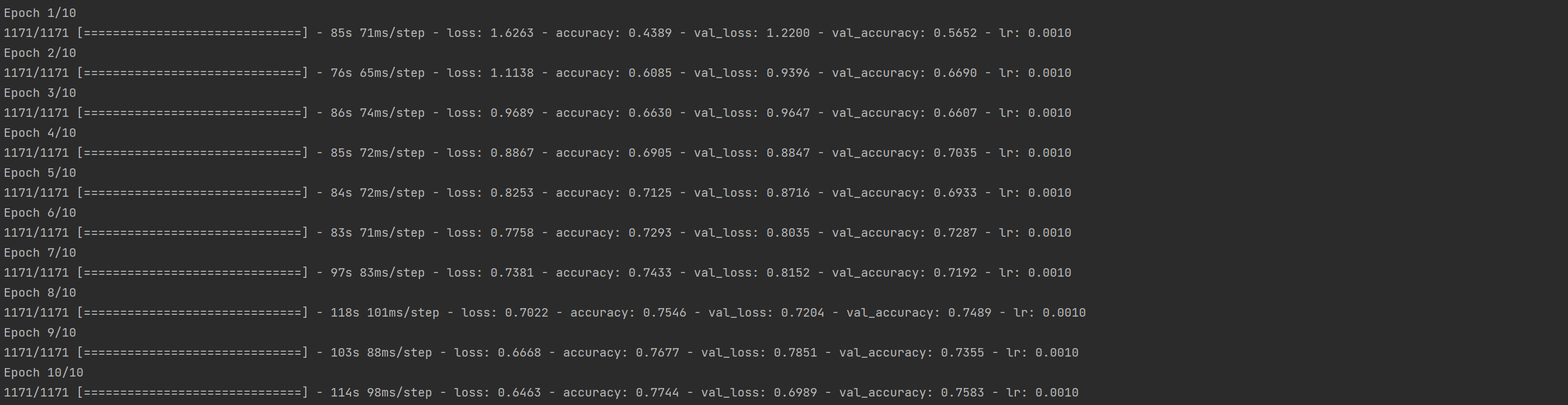
his=model.fit_generator(generator=train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=STEP_SIZE_TRAIN,
validation_data=valid_generator,
validation_steps=STEP_SIZE_VALID,
epochs=10, callbacks=callbacks
How to calculate steps:
Step 4: Model Evaluation
model.save("model_cifar_10epoch.h5")
acc=model.evaluate_generator(generator=valid_generator,steps=STEP_SIZE_VALID)
print(acc*100)

#Plot the training and valiation loss
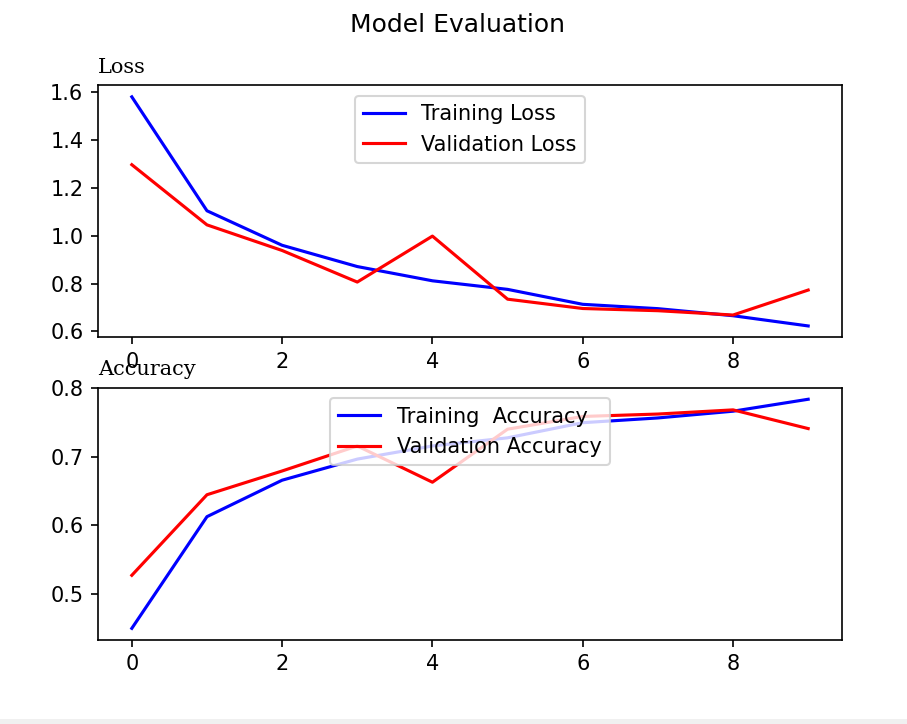
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2)
fig.suptitle('Model Evaluation')
#Assign the first subplot to graph training loss and validation loss
axs[0].plot(his.history['loss'],color='b',label='Training Loss')
axs[0].plot(his.history['val_loss'],color='r',label='Validation Loss')
axs[0].set_title('Loss', fontfamily='serif', loc='left', fontsize='medium')
axs[0].legend(loc='upper center')
#Next lets plot the training accuracy and validation accuracy
axs[1].plot(his.history['accuracy'],color='b',label='Training Accuracy')
axs[1].plot(his.history['val_accuracy'],color='r',label='Validation Accuracy')
axs[1].set_title('Accuracy', fontfamily='serif', loc='left', fontsize='medium')
axs[1].legend(loc='upper center')
plt.show()
Step 5: Generate Output
maps = {
0: 'airplane',
1: 'automobile',
2: 'bird',
3: 'cat',
4: 'deer',
5: 'dog',
6: 'frog',
7: 'horse',
8: 'ship',
9: 'truck'
}
test_generator.reset()
pred=model.predict(test_generator,steps=STEP_SIZE_TEST,verbose=1)
predicted_class_indices = np.argmax(pred, axis=1)
predictions = [maps[k] for k in predicted_class_indices]
filenames = test_generator.filenames
results = pd.DataFrame({"Filename": filenames,
"Predictions": predictions})
results.to_csv("model_cifar_10epoch.csv", index=False)